不管是mysql或者oracle等等数据库的连接,在我们Java程序中,都需要将相应的数据库驱动jar包加入到Java应用程序中
那么通过mybatis的两个DataSource数据源实现方式来看,我们的数据库驱动是如何加载的呢?
先来看mybatis的UnpooledDataSource.java数据源
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
* @author Eduardo Macarron
*/
public class UnpooledDataSource implements DataSource {
private ClassLoader driverClassLoader;
private Properties driverProperties;
private static Map<String, Driver> registeredDrivers = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Driver>();
/***
* 驱动类
*/
private String driver;
/***
* 数据库连接url
*/
private String url;
//用户名
private String username;
//密码
private String password;
//是否自动提交
private Boolean autoCommit;
//默认事务隔离级别
private Integer defaultTransactionIsolationLevel;
static {
//加载数据库驱动
//遍历获取依据注册的驱动类,并将该驱动类实例加入到当前数据源的缓存map中
Enumeration<Driver> drivers = DriverManager.getDrivers();
while (drivers.hasMoreElements()) {
Driver driver = drivers.nextElement();
registeredDrivers.put(driver.getClass().getName(), driver);
}
}
public UnpooledDataSource() {
}
//.....
}
按照mybatis的数据源实现方式,那么我们使用数据库的方式如下:
//创建数据源工厂
UnpooledDataSourceFactory unpooledDataSourceFactory=new UnpooledDataSourceFactory();
String driver="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true";
String username="root";
String password="123456";
//赋值properties
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.setProperty("driver",driver);
properties.setProperty("url",url);
properties.setProperty("username",username);
properties.setProperty("password",password);
unpooledDataSourceFactory.setProperties(properties);
//如果使用的是UnpooledDataSource数据源,则以上properties属性赋值需要使用UnpooledDataSource的属性值
//获取数据源
DataSource dataSource=unpooledDataSourceFactory.getDataSource();
Connection connection=dataSource.getConnection();
String sql="select * from user";
PreparedStatement pstm=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet rs=pstm.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()){
String id=rs.getString("id");
int age=rs.getInt("age");
String name=rs.getString("name");
System.out.println("id:"+id+",age:"+age+",name:"+name);
}
rs.close();
pstm.close();
connection.close();
这样我们会在控制台中打印当前user表的相关信息,看到这里,这在以前我会可能到此为止了,但是既然是源码研究,那么在阅读代码的时候就会产生疑问
疑问点:
static {
//加载数据库驱动
//遍历获取依据注册的驱动类,并将该驱动类实例加入到当前数据源的缓存map中
Enumeration<Driver> drivers = DriverManager.getDrivers();
while (drivers.hasMoreElements()) {
Driver driver = drivers.nextElement();
registeredDrivers.put(driver.getClass().getName(), driver);
}
}
在以上static块中,通过使用DriverManager.getDrivers()就能在Java程序中获取得到我们当前以及注册的数据库驱动Driver类,那么这些Driver类是何时注册的呢?
我们只能查看DriverManger.getDrivers()方法一探究竟.
@CallerSensitive
public static java.util.Enumeration<Driver> getDrivers() {
java.util.Vector<Driver> result = new java.util.Vector<>();
Class<?> callerClass = Reflection.getCallerClass();
//从registeredDrivers方法遍历得到Driver的Vector集合
// Walk through the loaded registeredDrivers.
for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {
// If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then
// skip it.
if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerClass)) {
result.addElement(aDriver.driver);
} else {
println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());
}
}
return (result.elements());
}
从registeredDrivers方法遍历得到Driver的Vector集合,所以,此段代码说明registeredDrivers一定是在某处已经初始化过,我们在代码上并没有其他调用,此时只能是DriverManager中存在static代码块
先来看部分代码:
public class DriverManager {
// List of registered JDBC drivers
private final static CopyOnWriteArrayList<DriverInfo> registeredDrivers = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
private static volatile int loginTimeout = 0;
private static volatile java.io.PrintWriter logWriter = null;
private static volatile java.io.PrintStream logStream = null;
// Used in println() to synchronize logWriter
private final static Object logSync = new Object();
/* Prevent the DriverManager class from being instantiated. */
private DriverManager(){}
/**
* Load the initial JDBC drivers by checking the System property
* jdbc.properties and then use the {@code ServiceLoader} mechanism
*/
static {
loadInitialDrivers();
println("JDBC DriverManager initialized");
}
}
果然,在static块中,存在loadInitialDrivers方法,顾名思义,这就是我们要找的驱动加载方法了.继续看下去.
private static void loadInitialDrivers() {
String drivers;
try {
drivers = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<String>() {
public String run() {
return System.getProperty("jdbc.drivers");
}
});
} catch (Exception ex) {
drivers = null;
}
// If the driver is packaged as a Service Provider, load it.
// Get all the drivers through the classloader
// exposed as a java.sql.Driver.class service.
// ServiceLoader.load() replaces the sun.misc.Providers()
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
ServiceLoader<Driver> loadedDrivers = ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class);
Iterator<Driver> driversIterator = loadedDrivers.iterator();
/* Load these drivers, so that they can be instantiated.
* It may be the case that the driver class may not be there
* i.e. there may be a packaged driver with the service class
* as implementation of java.sql.Driver but the actual class
* may be missing. In that case a java.util.ServiceConfigurationError
* will be thrown at runtime by the VM trying to locate
* and load the service.
*
* Adding a try catch block to catch those runtime errors
* if driver not available in classpath but it's
* packaged as service and that service is there in classpath.
*/
try{
while(driversIterator.hasNext()) {
driversIterator.next();
}
} catch(Throwable t) {
// Do nothing
}
return null;
}
});
}
从代码中我们看到通过ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class);
ServiceLoader是实现了Iterable迭代器的,来看类图
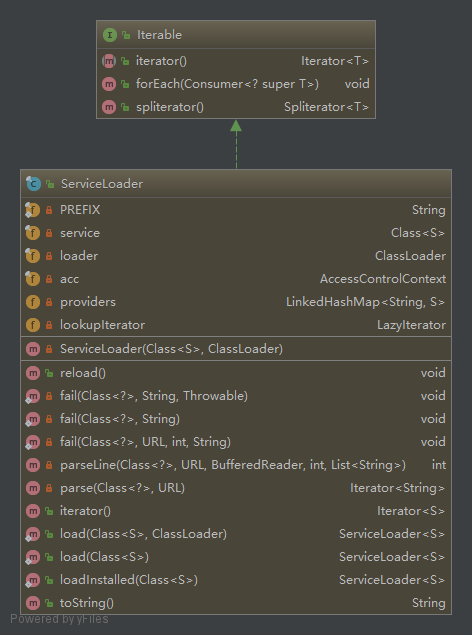
只提供了一个构造函数,根据Class和ClassLoader来构造ServiceLoader
//初始化ServiceLoader方法
public static <S> ServiceLoader<S> load(Class<S> service) {
ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
return ServiceLoader.load(service, cl);
}
public void reload() {
//情况
providers.clear();
lookupIterator = new LazyIterator(service, loader);
}
private ServiceLoader(Class<S> svc, ClassLoader cl) {
//Class 非空校验,如果为空 则抛出空指针异常.
service = Objects.requireNonNull(svc, "Service interface cannot be null");
//判断当前ClassLoader是否为空,如果为空,则使用系统默认ClassLoader
loader = (cl == null) ? ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() : cl;
acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null) ? AccessController.getContext() : null;
reload();
}
关于AccessController涉及到的方法,这里不做过多研究说明.
看了ServiceLoader的源码结构,在来看遍历
try{
while(driversIterator.hasNext()) {
driversIterator.next();
}
} catch(Throwable t) {
// Do nothing
}
此处的hasNext()方法实际调用的是ServiceLoader中的内部类LazyIterator中的hasNext()方法
来看LazyIterator类
private class LazyIterator
implements Iterator<S>
{
Class<S> service;
ClassLoader loader;
Enumeration<URL> configs = null;
Iterator<String> pending = null;
String nextName = null;
private LazyIterator(Class<S> service, ClassLoader loader) {
this.service = service;
this.loader = loader;
}
private boolean hasNextService() {
if (nextName != null) {
return true;
}
if (configs == null) {
try {
//获取资源路径名称因为传递过来的类是java.sql.Driver
//所以此处fullName的全称是:META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver
String fullName = PREFIX + service.getName();
if (loader == null)
configs = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fullName);
else
configs = loader.getResources(fullName);
} catch (IOException x) {
fail(service, "Error locating configuration files", x);
}
}
while ((pending == null) || !pending.hasNext()) {
if (!configs.hasMoreElements()) {
return false;
}
pending = parse(service, configs.nextElement());
}
nextName = pending.next();
return true;
}
private S nextService() {
if (!hasNextService())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
String cn = nextName;
nextName = null;
Class<?> c = null;
try {
c = Class.forName(cn, false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not found");
}
if (!service.isAssignableFrom(c)) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not a subtype");
}
try {
//从配置文件类中读取到驱动类Driver,通过反射调用产生Driver类的实例
S p = service.cast(c.newInstance());
providers.put(cn, p);
return p;
} catch (Throwable x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " could not be instantiated",
x);
}
throw new Error(); // This cannot happen
}
public boolean hasNext() {
if (acc == null) {
return hasNextService();
} else {
PrivilegedAction<Boolean> action = new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
public Boolean run() { return hasNextService(); }
};
return AccessController.doPrivileged(action, acc);
}
}
public S next() {
if (acc == null) {
return nextService();
} else {
PrivilegedAction<S> action = new PrivilegedAction<S>() {
public S run() { return nextService(); }
};
return AccessController.doPrivileged(action, acc);
}
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
通过hasNextService()方法,我们看到回去加载当前的资源
获取资源路径名称因为传递过来的类是java.sql.Driver 所以此处fullName的全称是:META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver
此时我们去查看mariadb的驱动及mysql的驱动jar包,看是否存在该文件
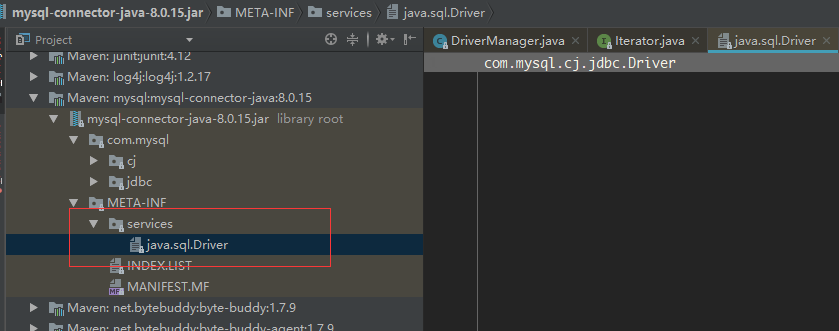
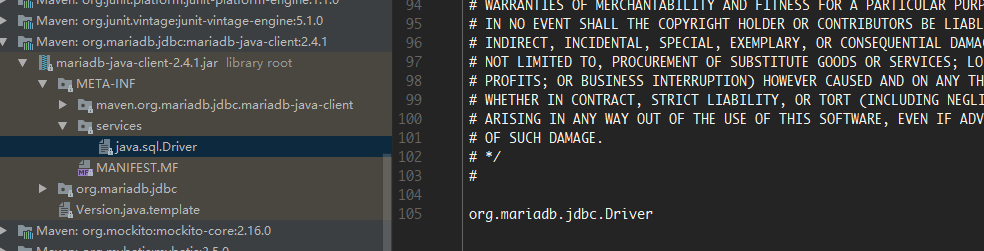
果然存在,代码看到这里,是否也能有个大概了呢?
看mysql的驱动代码
package com.mysql.cj.jdbc;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* The Java SQL framework allows for multiple database drivers. Each driver should supply a class that implements the Driver interface
*
* <p>
* The DriverManager will try to load as many drivers as it can find and then for any given connection request, it will ask each driver in turn to try to
* connect to the target URL.
*
* <p>
* It is strongly recommended that each Driver class should be small and standalone so that the Driver class can be loaded and queried without bringing in vast
* quantities of supporting code.
*
* <p>
* When a Driver class is loaded, it should create an instance of itself and register it with the DriverManager. This means that a user can load and register a
* driver by doing Class.forName("foo.bah.Driver")
*/
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
//
// Register ourselves with the DriverManager
//
static {
try {
//注册驱动
java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException E) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
/**
* Construct a new driver and register it with DriverManager
*
* @throws SQLException
* if a database error occurs.
*/
public Driver() throws SQLException {
// Required for Class.forName().newInstance()
}
}
看DriverManager.registerDriver方法
public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver,
DriverAction da)
throws SQLException {
/* Register the driver if it has not already been added to our list */
if(driver != null) {
//registeredDrivers
registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo(driver, da));
} else {
// This is for compatibility with the original DriverManager
throw new NullPointerException();
}
println("registerDriver: " + driver);
}
registeredDrivers集合在此处得到初始化
我们回过头来再看LazyIterator迭代器中的方法
private S nextService() {
if (!hasNextService())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
String cn = nextName;
nextName = null;
Class<?> c = null;
try {
c = Class.forName(cn, false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not found");
}
if (!service.isAssignableFrom(c)) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not a subtype");
}
try {
//从配置文件类中读取到驱动类Driver,通过反射调用产生Driver类的实例
S p = service.cast(c.newInstance());
providers.put(cn, p);
return p;
} catch (Throwable x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " could not be instantiated",
x);
}
throw new Error(); // This cannot happen
}
从配置文件类中读取到驱动类Driver,通过Class.forName方法将该类加载到JVM中,此时会调用执行Driver类中的static方法块,将Driver类驱动注册到DriverManager中。整个过程到此完结。

